Bookings, billings, and revenue are often used interchangeably in the dynamic business landscape.
However, understanding their differences is vital for assessing a company’s:
- Financial health
- Predicting growth
- Guiding business strategies
As a startup, Saas, or entrepreneur, you must know them and figure out where to apply them to make the most of your company.
This comprehensive guide delves into the definitions, significance, and practical implications of bookings, billings, and revenue in businesses.
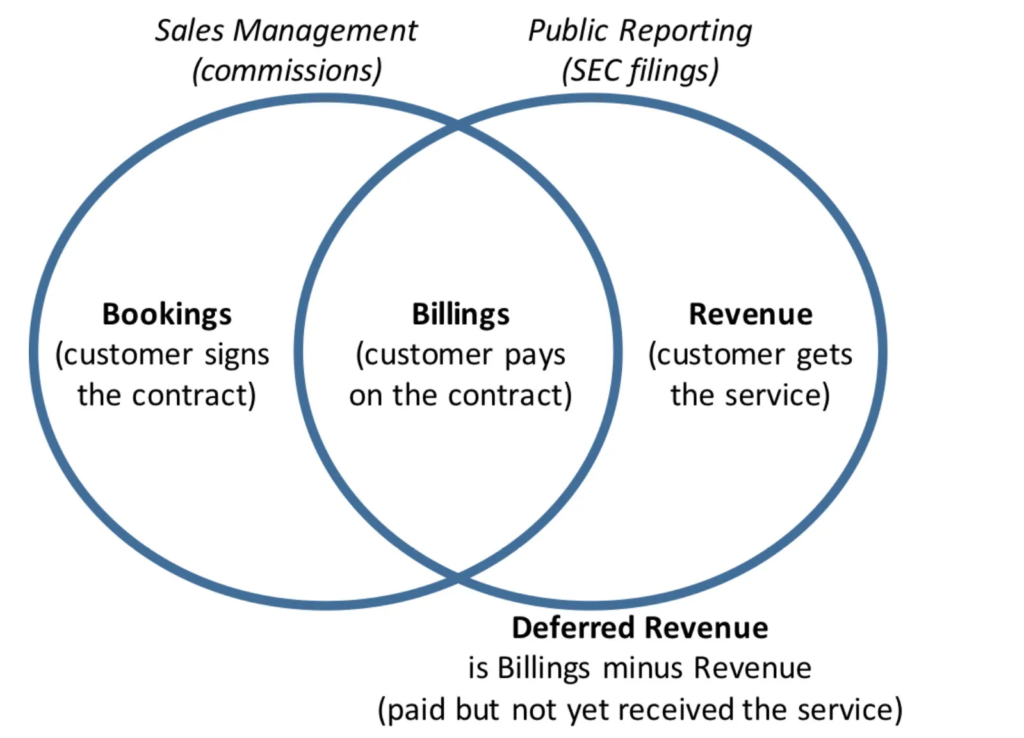
Source: Softwareplatform
Bookings
Bookings in the SaaS business refer to when a customer ‘books’ a product or service, committing to spend money on it.
It’s a forward-looking metric that provides insights into the company’s revenue growth and financial health.
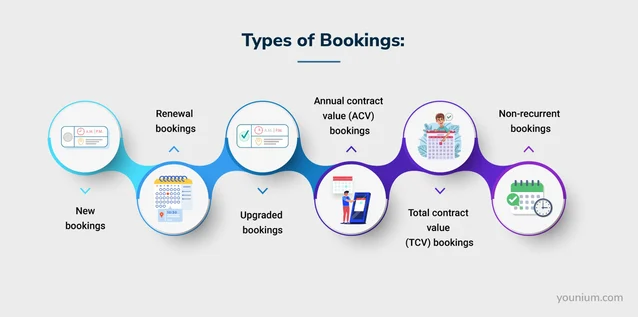
There are three types:
- New Bookings: When a new customer books a product or service.
- Renewal Bookings: When an existing customer renews a subscription to a product or service they already use.
- Upsell Bookings: When existing customers expand their purchase, subscribing to a more extensive package.
- Annual Contract Value Booking: When a customer commits to a yearly subscription for a product or service, indicating the revenue expected from that contract for one year.
- Total Contract Value Booking: When a customer commits to a subscription for a product or service, indicating the total revenue expected from that contract over its entire duration.
- Non-recurrent Booking: When a customer makes a one-time purchase of a product or service without any commitment to future renewals or subscriptions.
Analyzing bookings helps to understand the direction of the company’s revenue growth. A higher ratio and more excellent value signify successful delivery of the business message to prospective customers.
However, it’s essential to note that multi-year contracts cannot be included as revenue, as they represent future commitments.
Source: Younium
Billings
Billing is the next stage after booking, where the money is collected from customers who have booked a product or service.
Unlike bookings, which are about commitments, billings are about actual cash flow.
Businesses that bill their customers upfront have better-managed cash flow at the time of booking.
Billings do not directly translate into revenue. It can only be recognized if a product or service is delivered. They remain a liability in the balance sheet until delivery, making billings crucial for assessing cash flow.
Analyzing its status helps understand the company’s position and potential cash flow issues.
Revenue
Revenue is the last stage, where the company recognizes the billed amount as its revenue and delivers the products or services paid for. It’s the actual amount earned.
For example, you’d have to use the GAAP standards for a SaaS. GAAP is a collection of generally accepted accounting rules in the U.S. that ensures consistency in financial reporting. They were established by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) to help investors and regulators understand and compare financial statements across companies.
Now, as a subscription-based product, revenue is recognized over the lifetime of the subscription, not only at the beginning.
Revenue demonstrates the position of a business’s performance. Relying solely on booking or billing stage data may lead to inflated numbers that may not reflect the company’s financial situation.

Source: Younium
Booking, Billing, and Revenue Real-Life Example
Imagine a company named “SoftTech Solutions” that offers a premium software package for $1200 per year.
On January 1st, a customer named John purchased a yearly subscription. This commitment represents future revenue for SoftTech Solutions, even though no money has changed hands yet.
When John agrees to the subscription, SoftTech Solutions has a “booking” of $1200.
| Date | Event | Amount | Description |
| January 1 | John commits to a yearly subscription. | $1200 | SoftTech Solutions has a “booking” for an annual subscription worth $1200. |
After John commits to the subscription on January 1st, SoftTech Solutions sends him an invoice for $1200. John paid the invoice on January 5th. This is the “billing” event.
SoftTech Solutions now has the cash in hand, but it’s important to note that they haven’t recognized this as revenue yet because they haven’t provided John with the entire year of software service.
| Date | Event | Amount | Description |
| January 1 | John commits to a yearly subscription. | $1200 | SoftTech Solutions has a “booking” for an annual subscription worth $1200. |
| January 5 | John pays the invoice. | $1200 | SoftTech Solutions receives the payment, marking the “billing” event. |
As SoftTech Solutions provides its software service to John over the year, it will gradually recognize the $1200 as “revenue.”
Let’s assume the service is delivered evenly over the year. By the end of January, SoftTech Solutions would recognize $100 ($1200 divided by 12 months) as revenue for that month.
By the end of the year, the full $1200 would be recognized as revenue, reflecting the actual amount earned by SoftTech Solutions for providing its service to John for the entire year.
| Month | Amount Recognized as Revenue | Acumulative Revenue | Description |
| January | $100 | $100 | January services |
| February | $100 | $200 | February services |
| March | $100 | $300 | March services |
| April | $100 | $400 | April services |
| May | $100 | $500 | May services |
| June | $100 | $600 | June services |
| July | $100 | $700 | July services |
| August | $100 | $800 | August services |
| September | $100 | $900 | September services |
| October | $100 | $1000 | October services |
| November | $100 | $1100 | November services |
| December | $100 | $1200 | December services |
Impact on Financial Reports
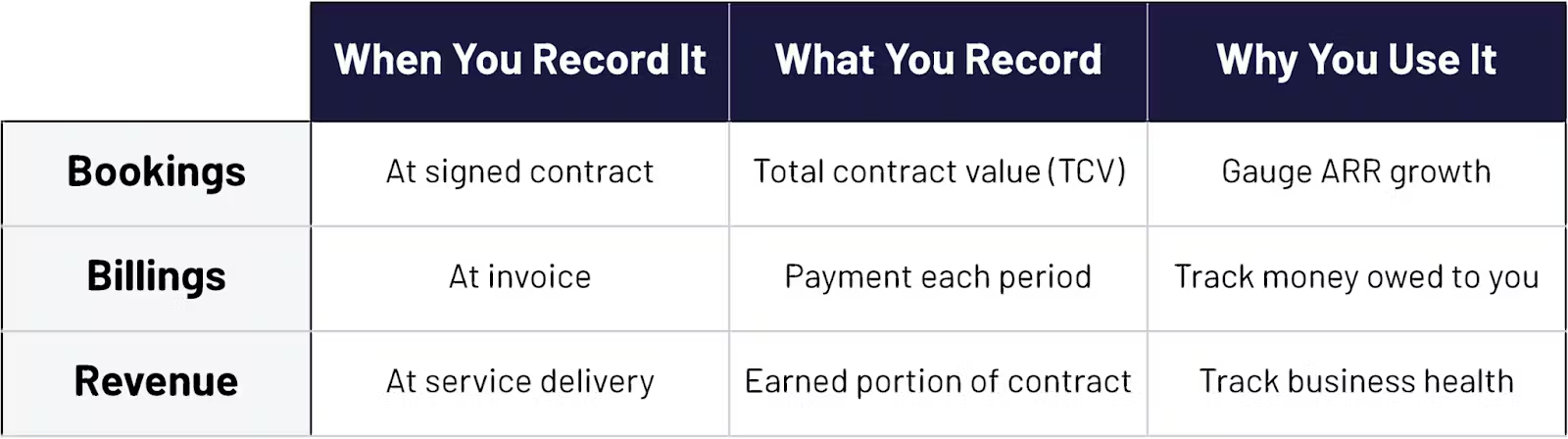
The most notable difference between Bookings, Billings & Revenue is the impact on financial reports due to their distinct stages in the economic life cycle of a transaction and the way they are recognized in accounting.
- Bookings do not directly impact financial reports or income statements.
- Billings impacts the cash flow, balance, and income statements.
- Revenue recognition affects the balance sheet and income statement, as it’s the stage where income is realized.
Understanding the differences between them is vital for making informed decisions, not only in financial matters but also in other areas of business operation. For instance, you could find performance gaps to improve revenue-generating capacity.
Source: Mosaic
Practical Implications for Startups
Startups must navigate a complex financial landscape, particularly in the technology and SaaS sectors.
Knowing the nuances of bookings, billings, and revenues is more than just a matter of compliance or accounting. It has far-reaching practical implications that can shape the entire trajectory of a startup.
Here’s how these metrics help startups:
- Aligning Sales and Marketing Strategies: The flow from bookings to billings to revenue helps align sales and marketing strategies. When analyzing the metrics, startups can identify what’s working and what’s not, allowing them to allocate resources more effectively.
- Cash Flow Management: Startups often operate on tight budgets, and cash flow management is crucial. They can forecast cash flow more accurately, ensuring their needed funds to work and grow.
- Investor Relations: Stakeholders are keenly interested in a startup’s financial metrics. A correct metric report will build investor confidence and facilitate fundraising efforts.
- Compliance and Legal Considerations: Startups must adhere to various accounting standards, including GAAP. Properly recognizing bookings, billings, and revenues ensures compliance and avoids potential legal issues.
- Strategic Planning: These metrics are vital for strategic planning. Bookings provide a glimpse into future growth, billings reflect cash flow, and revenues show actual earnings. Together, they provide a comprehensive picture that can guide long-term strategies.
- Performance Evaluation: Evaluating the performance of different departments, especially sales and marketing, requires a clear understanding of these metrics. Not doing so leads to incorrect evaluations and misguided incentives.
- Risk Management: It helps you to identify potential risks and vulnerabilities in the business model. For example, a high deferred revenue level might indicate potential future cash flow problems.
- Enhancing Customer Relationships: By tracking bookings, billings, and revenues, startups can gain insights into customer behavior and preferences. This information improves customer relationships and increases retention.

Source: Investopedia
How Bookings, Billings, And Revenue Guide Business Strategies
These metrics provide vital information that helps plan payments, commissions, and variable compensations. They are crucial for making the right decisions in various business matters.
Bookings, billings, and revenue offer a comprehensive view of a company’s financial landscape, each shedding light on different facets of the business.
Businesses can align their strategies to:
- Find better functionalities.
- Optimize resources.
- Enhance customer relationships.
- Succeed in a competitive marketplace.
This will allow them to navigate the financial landscape with confidence and foresight.
Effective Strategies for Bookings, Billings, & Revenue
Here are four effective management strategies for each metric that businesses should use to control their finances:
Bookings Management Strategies
- Forecasting and Planning: Utilize historical data and market trends to forecast future bookings, assisting in resource allocation and strategic planning.
- Segmentation Analysis: Break down bookings by product, region, or customer type to identify growth opportunities and areas for improvement.
- Sales Alignment: Align sales targets and incentives with booking goals to motivate the sales team and drive growth.
- Technology Integration: Implement CRM and other tools to automate and track the booking process, ensuring accuracy and efficiency.
Billings Management Strategies
- Automated Invoicing: Employ automated billing systems to ensure timely and accurate invoicing, reducing errors and enhancing cash flow.
- Flexible Payment Terms: Offer various payment options and terms to accommodate different customer needs, improving customer satisfaction and payment timeliness.
- Compliance Monitoring: Ensure adherence to tax laws, regulations, and contractual obligations to minimize legal risks.
- Aging Analysis: Regularly review accounts receivable aging reports to identify potential collection issues and take proactive measures.
Revenue Management Strategies
- Revenue Recognition Compliance: Use relevant accounting standards (GAAP or IFRS) for accurate and ethical revenue recognition.
- Diversification: Develop diverse revenue streams to mitigate risks and ensure stability, especially in volatile markets.
- Customer Retention Focus: Implement strategies to enhance customer satisfaction and retention, as retaining existing customers leads to more predictable and sustainable revenue.
- Performance Monitoring: Utilize KPIs and dashboards to continuously monitor revenue performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
Advanced Metrics and KPIs
For industries like SaaS, worth over $195 billion, where the business model is built around recurring revenue and long-term customer relationships, understanding advanced metrics such as Deferred Revenue, Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR), and Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) is vital.
They improve the company’s financial health and offer valuable insights such as:
- Customer behavior.
- Product performance.
- Market trends.
Deferred Revenue
Deferred revenue is a critical financial concept in the SaaS business model. It represents the money billed but not recognized as revenue because the service has yet to be provided.
When a customer pays for a subscription, the entire amount cannot be recognized as revenue immediately. Instead, it must be recognized over the subscription’s lifetime.
For example, if a customer pays $12,000 yearly, the company can only recognize a portion of it as monthly revenue as the service is delivered. The rest is put into a deferred revenue account until the service is fully provided.
This metric is essential for accurate financial reporting and compliance with GAAP standards. It ensures that revenue is recognized only when earned, reflecting the actual financial health of the business.

Source: WallStreetMojo
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
MRR measures the monthly recurring revenue expected. It includes subscriptions, monthly fees, and other recurring charges.
Here is why this is essential:
- Predictability: It offers a predictable revenue stream, allowing businesses to plan and budget effectively.
- Growth Tracking: Companies can identify trends and assess the effectiveness of sales and marketing strategies.
- Cash Flow Management: Understanding MRR helps manage cash flows, ensuring the business has sufficient funds to operate.
MRR provides insights into the company’s growth rate, stability, and future revenue projections.
MRR formula: MRR = MS x ARPU
Meaning:
MRR = Total Monthly Recurring Revenue
ARPU = Average Revenue Per User
MS = Monthly Subscribers
Source: Younium
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR)
ARR is similar to MRR but represents the value of the recurring revenue components of your subscriptions over a year, and here is why this is essential:
- Long-term Planning: ARR provides a broader view of the company’s revenue, aiding in long-term planning and strategy development.
- Investor Attraction: It makes the company more attractive by demonstrating consistent revenue growth.
- Resource Allocation: Understanding it helps allocate resources efficiently, ensuring that the business invests in areas that contribute to recurring revenue.
ARR formula: ARR = MRR x 12

Source: Profit.co
Common Pitfalls Startups Face while Differentiating Bookings, Billings, and Revenues
Misunderstanding these terms can lead to incorrect analysis and decision-making, affecting the overall business performance.
Be aware of the following pitfalls:
- Confusing Terms: Misunderstanding the definitions of bookings, billings, and revenues can lead to incorrect financial reporting and forecasting.
- Overemphasis on Bookings: Focusing too much on bookings without considering billings and revenue can create a misleading picture of financial health.
- Ignoring GAAP Standards: Failure to follow GAAP standards in revenue recognition can lead to compliance issues.
- Lack of Alignment with Sales and Marketing: Misalignment between financial metrics and sales/marketing goals can hinder growth strategies.
The US has approximately 8x more SaaS companies than any other country. Here’s how the GAAP requirements look by state:
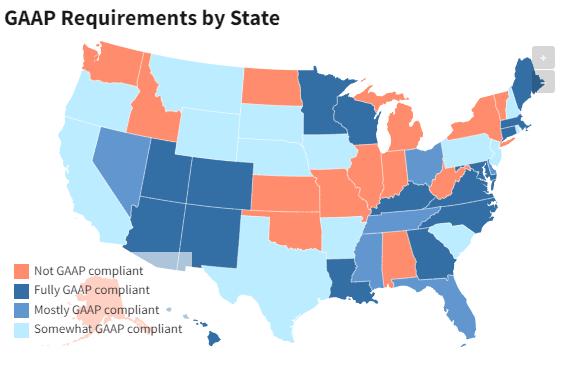
Source: Investopedia
Best Practices for Accurate Tracking And Reporting
Understanding and utilizing these financial terms separately and in combination can enhance business performance analysis and decision-making.
Here are the best practices to consider:
- Clear Definitions: Ensure that everyone in the organization understands the differences between bookings, billings, and revenues.
- Regular Monitoring: Track these metrics to identify trends and make informed decisions.
- Alignment with Business Goals: Align them with overall business goals to ensure cohesive growth strategies.
- Compliance with Standards: Adhere to GAAP standards in revenue recognition to maintain compliance.
Tools And Software Solutions Beneficial for Startups
Investing in tools that help track and analyze these metrics can be a game-changer for startups. Here are some software that you can use:
- Accounting Software: Tools like QuickBooks or Xero can automate the tracking of bookings, billings, and revenues.
- Analytics Platforms: Platforms like Tableau provide visual insights into financial data, aiding analysis.
- Integration with CRM: Integrating financial tools with CRM systems ensures alignment with sales and marketing. Ensure you have the best CRM software.
Recommended Courses And Workshops on Financial Metrics
Educating the team through courses and workshops can foster a deeper understanding of these financial metrics.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and Udemy offer courses on financial metrics and accounting tailored to startups.
- Workshops and Seminars: Regularly attending industry workshops can keep the team updated on the latest best practices. You could visit the Saas Academy for more information.
- In-house Training: Consider developing in-house training programs to ensure that all team members understand these critical financial concepts. You’d have to find companies looking for trainees and get hired to receive proper knowledge.
Future Trends
The future is an uncertain place. Yet, we can surely agree that business technologies will continue to evolve. For example, Big data is considered the next big tool to help businesses succeed, with 72% claiming some importance.
Still, there are other trends that you should follow:
- AI and Machine Learning: Using AI in financial tracking can provide predictive insights and help you automate complex analyses.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain can enhance transparency and security in financial reporting.
- Real-time Analytics: The trend towards real-time financial analytics will continue to grow, providing instant insights into financial health.
Challenges and Mistakes to Avoid
There are three main challenges startups, SaaS, and entrepreneurs face when dealing with bookings, billings, and revenue:
- Avoid One-Size-Fits-All Approach: Recognize that bookings, billings, and revenues are distinct and require separate tracking and analysis.
- Avoid Over-Reliance on Tools: While tools are helpful, human oversight and understanding are essential for accurate interpretation.
- Learn from Others: Case studies of startups that faced difficulties due to misunderstandings of these metrics can provide valuable lessons. Engage with mentors and industry experts to avoid common mistakes.
FAQs
How Do Refunds and Cancellations Affect Billings and Revenue?
Refunds and cancellations lead to a reduction in billings and may require adjustments in recognized revenue.
Proper policies and procedures should be in place to handle these situations and ensure accurate financial reporting.
How Do You Convert Bookings To Revenue?
Companies convert bookings into revenue when they fulfill customer obligations in sales contracts.
For example, a company’s bookings might include a deal to supply different products over time, each priced individually. After the delivery of each product, the company recognizes the revenue allocated to that product in the contract.
How Can Companies Ensure Accurate Billing and Revenue Matching?
Companies can adopt robust accounting and billing systems, conduct regular audits, and train their finance teams in best practices.
Ensuring that billings match the revenue recognized is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance.
Can Billings Be Used as a Predictor for Customer Loyalty?
Yes, analyzing billing patterns can reveal insights into customer loyalty. Consistent and timely billings indicate satisfied customers, while erratic patterns signal potential issues.
Wrapping Up
Bookings, billings, and revenue are distinct yet interrelated terminologies that play a crucial role in SaaS businesses.
By understanding their differences and practical implications, owners and executives can make informed decisions to improve performance and revenue-generating capacity.
These are financial reporting tools and strategic assets for growth and success in the competitive SaaS landscape.
Use them wisely and find the best combinations to control your business’s financial status.
