When angel investors, venture capital, or strategic partners consider investing, it usually involves several steps. They’ll meet with you, and you’ll likely have to present your business proposal. There will be a series of questions and discussions. If everything looks promising, the next stage is due diligence for your startup.
Now, here’s the thing – due diligence can vary from investor to investor. Each one has its own criteria and areas of focus. Some might be interested in your intellectual property, while others want to explore your growth potential.
This process can be complex and challenging, but with the right preparation, it can be navigated effectively. Our guide provides clear, step-by-step instructions to help you prepare for a due diligence process, ensuring you’re ready to present your startup in the best possible light. With careful planning and organization, you can approach this critical business phase with confidence and poise.
Where and How Did It Begin: A Brief History of Due Diligence
Due diligence originated with the Securities Act of 1933 in the United States, which mandated securities dealers and brokers to disclose all material information about the instruments they sold. This law aimed to protect investors from fraud. However, to prevent dealers and brokers from facing unfair prosecution for information they couldn’t have known, the act introduced the concept of “due diligence.” If they thoroughly investigated the companies they were dealing with and disclosed the findings, they couldn’t be held liable for undiscovered information during the investigation.
| According to Thomson Reuters, due diligence is a process where a potential buyer or investor conducts a thorough investigation of a company, asset, or business. The purpose of this investigation is to assess the value of the asset, uncover any potential issues, and gather additional information that could influence the investment or the negotiation of terms. This process is crucial in mitigating risks associated with the investment. |
Why Is Due Diligence Important for Startups?
Startup due diligence involves thoroughly investigating, auditing, and analyzing startup companies before making an investment. The objective is to obtain comprehensive information about the target company, especially any factors potentially devaluing it.

Source: Google
The motivations behind conducting due diligence for startups are similar to those of any other due diligence process. The goal is to gain a complete understanding of the startup’s operations, finances, legal status, and potential risks to make an informed investment decision.
For startups, undergoing due diligence allows them to demonstrate to investors that their company is well-organized and prepared for investment. Investors recognize the importance of growth but also seek reassurance that the company can effectively manage its operations as it expands.
Different Types of Due Diligence Depending on the Purpose:
- Context-Specific Due Diligence: This includes commercial due diligence, which assesses a company’s market share, competitive positioning, future prospects, and growth opportunities. It also examines the supply chain, market analysis, sales pipeline, R&D pipeline, and overall operations, including management, human resources, and IT.
- Legal Due Diligence: This focuses on ensuring that a company complies with all legal, regulatory, and compliance requirements. It involves reviewing pending litigation and intellectual property rights and confirming proper incorporation.
- Financial Due Diligence: This type of due diligence involves an in-depth audit of a company’s financial statements and books to ensure there are no irregularities and to assess the company’s financial stability.
- Tax Due Diligence: Here, the focus is on examining the company’s tax exposure, potential back taxes owed, and opportunities for reducing the tax burden in the future.
Due diligence can be divided into two categories: “hard” and “soft” based on the approach used.
Hard Due Diligence:
This approach focuses on the financial numbers and data found in the company’s financial statements, such as the balance sheet and income statement. It involves fundamental analysis and the use of financial ratios to understand the company’s financial position and make future projections. Hard due diligence is effective in identifying red flags and accounting inconsistencies. However, it is vulnerable to biased interpretations, as eager salespeople may present the numbers positively. To counter this, soft due diligence provides a more qualitative perspective.
Soft Due Diligence:
This approach takes a qualitative view, examining aspects like the quality of management, the people within the company, and the loyalty of its customer base. It recognizes that there are critical drivers of business success that cannot be fully captured by numbers alone, such as employee relationships, corporate culture, and leadership. Soft due diligence is crucial because, in many cases where M&A deals fail (around 70%-90% of them), it is often due to the neglect of the human element.
Legal Ramifications of Due Diligence for Startups
- Companies that lie during the due diligence process can face legal consequences. Investors usually have contracts with warranties and legal recourse for misrepresentation, allowing them to sue if false information is discovered later.
- Popular investment types, such as the SAFE note, include clauses that require the company to provide truthful information during due diligence. This binds the company to be honest about its IP, materials, and legal standing.
- Medical start-up Theranos, claimed to revolutionize blood testing with innovative technology, but instead delivered inaccurate diagnoses to patients and misled investors, leading to legal consequences. Severe misrepresentations, like in the case of Theranos, can lead to criminal penalties for selling securities without full disclosure.
Entrepreneurs should take due diligence seriously and consider hiring outside counsel and accountants to ensure they provide accurate and verifiable data. Providing truthful information is crucial for protecting founders personally and safeguarding the company’s assets.
Here is a real life example that discusses the legal ramifications of due diligence for a startup:
JP Morgan Says Startup Founder Used Millions Of Fake Customers To Dupe It Into An Acquisition by Alexandra S. Levine and Iain Martin: This article discusses a case where JPMorgan Chase sued the founder of a startup it acquired for allegedly lying about its scale and success. The startup, Frank, was accused of creating an enormous list of fake users to entice the financial giant to buy it. When JP Morgan asked for proof during due diligence, the founder allegedly created an enormous roster of “fake customers”. In reality, according to the suit, Frank had fewer than 300,000 customer accounts at that time. The founder faced legal consequences for these actions.
What Do Investors Ask for During Due Diligence?
Here’s a list of the information investors typically ask for during the due diligence process for startups:
- Financials: Investors will request historical financial records, including the balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statements, and general ledger. They want to assess the company’s financial health, profitability, liquidity, and overall financial stability. The financial statements offer insights into the company’s revenue, expenses, assets, and liabilities, helping investors understand the financial performance and potential risks.
- Intellectual Property: Investors need evidence that the startup has the rightful ownership or rights to the intellectual property (IP) it claims to have. This includes patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and other proprietary assets. Validating IP ownership is crucial to ensure that the company’s products or services are protected and not vulnerable to legal challenges from competitors.
- Corporate Documents: Investors want to ensure that the startup has the appropriate legal structure and is compliant with regulations. They may ask for articles of incorporation, letters of good standing, and annual meeting notes to verify the company’s legal status and adherence to corporate governance standards.
- Outstanding Litigation: Disclosure of any ongoing lawsuits and potential legal issues is essential during due diligence. Investors need to assess the potential impact of litigation on the company’s financial health and reputation.
- Employees and Founders: The strength and expertise of the team are critical factors in a startup’s success. Investors will inquire about the key employees and founders to assess their qualifications, experience, and commitment to the venture. A skilled and dedicated team is more likely to execute the business plan effectively.
- Customer and Supplier Information: Understanding the company’s key customers and suppliers is vital for investors. They want to know if the business relies heavily on a few customers or if it has diversified revenue streams. Knowing about critical suppliers helps evaluate potential supply chain risks.
- Revenue Streams: Investors will dive into the details of the company’s revenue streams. They may inquire about metrics like churn rate (customer turnover), customer acquisition cost, customer lifetime value, and pricing strategy. This analysis helps them gauge the stability and growth potential of the revenue streams.
- Business Model and Projections: Investors will examine the startup’s business model and evaluate its viability and scalability. They will review the company’s projections and forecasts to ensure they are realistic, achievable, and supported by sound assumptions.
- Cap Table: The capitalization table overviews the company’s ownership structure and equity distribution. Investors analyze the cap table to assess how much ownership they will have and if the company’s equity has been diluted by previous funding rounds.
- Market: Thorough market research is critical during due diligence. Investors will want to know the size of the target market, market trends, competitive landscape, and the startup’s market share. Understanding the market dynamics helps investors assess the growth potential and market positioning of the startup.
Venture Capital Due Diligence Process
Venture capital firms play a pivotal role in nurturing and accelerating the growth of innovative startups. Before making significant investment decisions, these firms meticulously scrutinize potential investment targets through a rigorous due diligence process.

9 Step Guide for Startups to Navigate Through the Process of Due Diligence:
Properly preparing for due diligence is essential as it can significantly impact the investor’s decision to fund the startup.
In this comprehensive step-by-step guide, we will explore the key actions and strategies that startups should undertake to ensure a smooth and successful due diligence process.
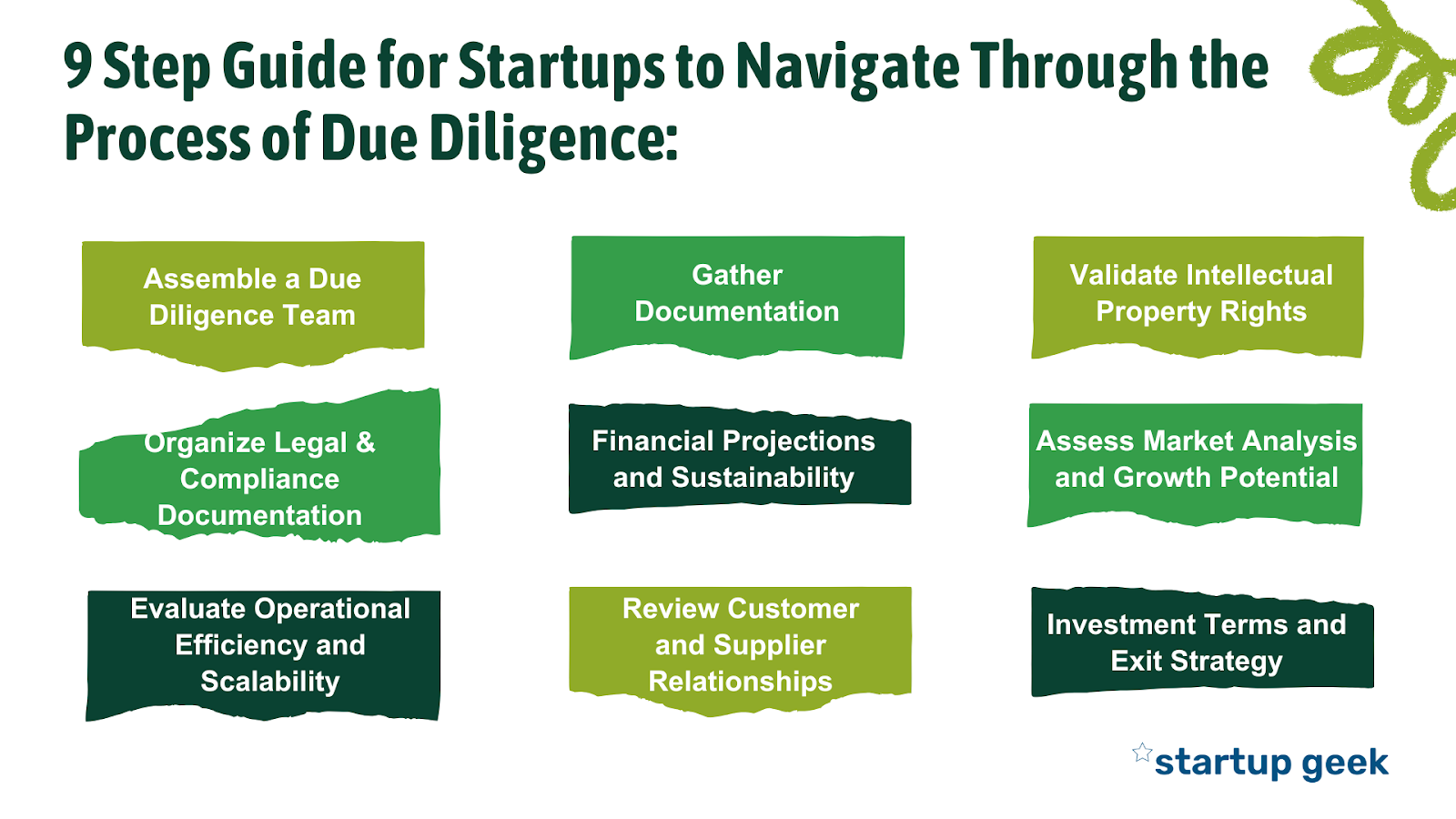
Step 1: Assemble a Due Diligence Team
Assembling a dedicated due diligence team is a critical first step for startups preparing for the due diligence process. This team will be pivotal in organizing, coordinating, and presenting information to potential investors.
Identify Key Team Members:
Start by identifying key team members who will be involved in the due diligence process. This may include founders, senior executives, financial experts, legal advisors, and other relevant stakeholders with in-depth knowledge of the company’s operations and financials.
Assign Roles and Responsibilities:
Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each team member. Designate a point of contact or project manager responsible for overseeing the due diligence efforts and coordinating communication between team members.
Create a Cross-Functional Team:
Due diligence covers various aspects of the startup, from financials and legal matters to market potential and operations. Therefore, it’s crucial to create a cross-functional team that combines expertise from different areas to address all aspects comprehensively.
Set Expectations and Timelines:
Communicate the importance of the due diligence process to the team and set clear expectations regarding the level of effort required. Establish realistic timelines for completing the various tasks and ensure that team members are committed to meeting these deadlines.
Ensure Access to Information:
Ensure that the due diligence team has access to all necessary information and documents. This may involve consolidating data from different departments and systems to create a comprehensive repository of information.
Encourage Collaboration and Communication:
Foster a culture of collaboration and open communication within the due diligence team. Encourage team members to share insights, ask questions, and seek assistance from colleagues when needed.
Step 2: Gather Documentation
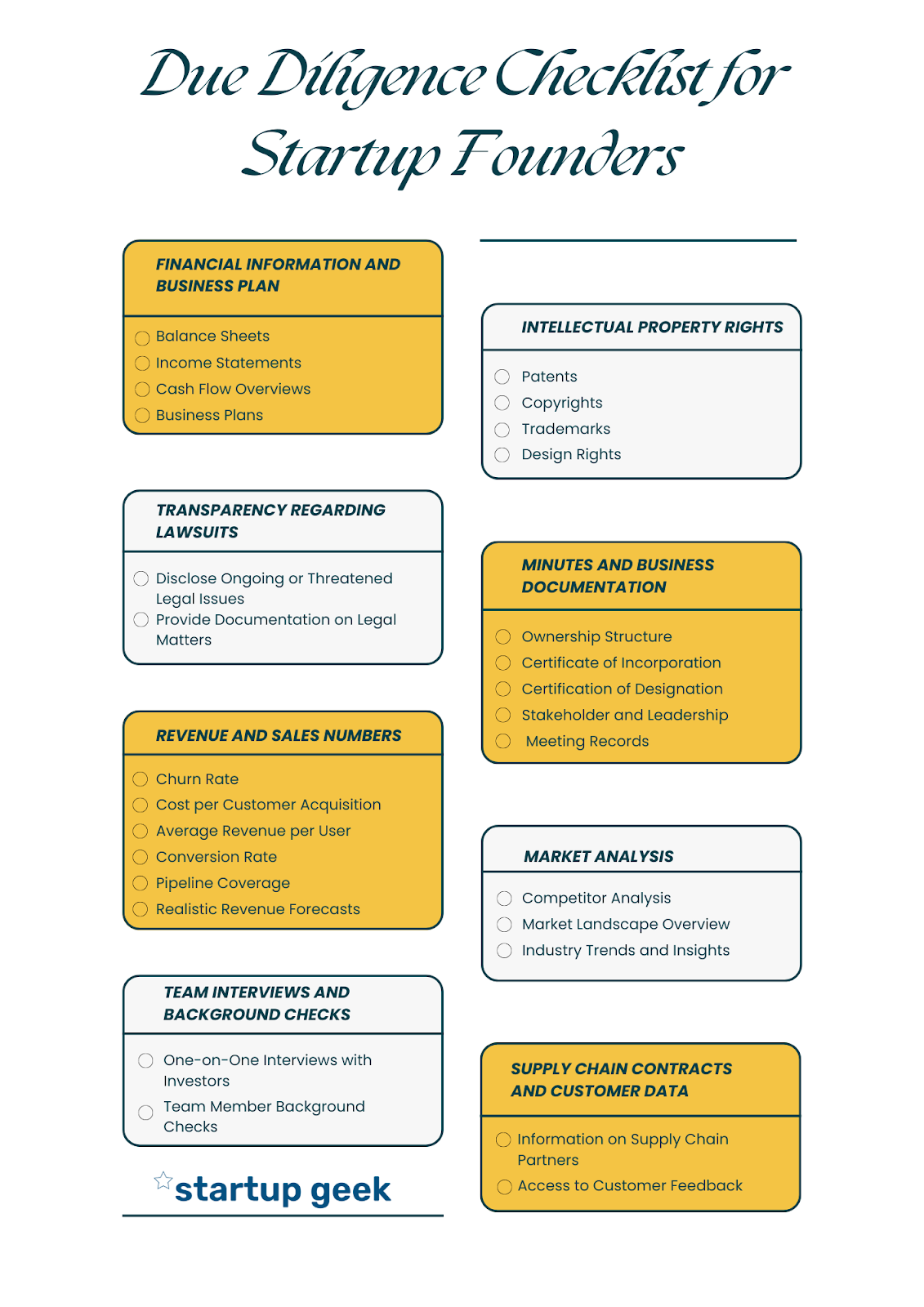
The next crucial step is to gather an extensive array of documentation that will provide potential investors with a comprehensive and transparent view of the startup’s operations, financials, and legal standing. By assembling a well-organized collection of essential documents, startups can instill confidence in investors, demonstrate their readiness for scrutiny, and pave the way for fruitful investment discussions.
Here are the key documents that startups must compile to navigate the due diligence process with ease and credibility.
- Financial Records
- Legal Agreements and Contracts
- Intellectual Property (IP) Documentation
- Regulatory Filings and Compliance Records
- Market Research and Customer Data
- Business Plan and Strategy
- Financial and Accounting Policies
- Insurance Coverage
- Employee Information
Step 3: Validate Intellectual Property Rights
Potential investors are keen to ensure that the startup has the necessary rights to its IP, minimizing the risk of legal disputes and safeguarding the uniqueness of the products or services offered.
Here are the essential steps for startups to validate their intellectual property rights during due diligence:
- Patent and Trademark Analysis: Review the startup’s patent portfolio and trademark registrations, ensuring they are in force, align with its products, and are not subject to infringement claims.
- Copyright and Trade Secrets Protection: Validate copyright protection for creative works and establish measures to safeguard trade secrets and confidential information.
- License Agreements and Domain Name Ownership: Verify the terms of any license agreements and confirm ownership of domain names related to the startup’s brand.
- Infringement Assessments and IP Transferability: Perform infringement assessments to identify potential conflicts and verify the transferability of IP rights in case of acquisitions or mergers.
- Record Keeping and Future IP Strategy: Maintain organized records of all IP-related documents and outline the startup’s future IP strategy to maintain a competitive edge.
Step 4: Organize Legal and Compliance Documentation
Amidst the due diligence process, potential investors scrutinize a startup’s legal standing and compliance with applicable laws and regulations. Thoroughly organizing legal and compliance documentation is vital to instill investor confidence and mitigate any potential legal risks. A well-documented and legally compliant startup conveys professionalism and transparency, paving the way for smoother investment negotiations.
Here are the key steps for startups to organize their legal and compliance documentation during due diligence:
Company Formation and Governance:
Provide all documentation related to the startup’s formation, such as articles of incorporation, certificates of formation (for LLCs), and bylaws. This is to verify that the company has been legally established and follows appropriate governance procedures.
Shareholder and Ownership Structure:
Present a clear overview of the startup’s ownership structure. This should include details of shareholders, percentage ownership, and any existing agreements among shareholders. It’s important to ensure that all ownership transfers and equity issuances are well-documented.
Contracts and Agreements:
Gather all relevant contracts and agreements entered into by the startup. This could include customer contracts, vendor agreements, licensing agreements, and partnership contracts. Review these documents to ensure compliance with legal requirements and identify any potential risks.
Litigation and Legal Proceedings:
Disclose any ongoing or past litigation involving the startup, including lawsuits, arbitration, or regulatory actions. It’s important to address how these legal matters have been resolved or are being handled.
Step 5: Financial Projections and Sustainability
Demonstrating a well-thought-out and realistic financial forecast can instill confidence in investors and pave the way for successful investment discussions.
Here are the key points to consider when presenting financial projections during due diligence:
- Comprehensive Revenue Forecast: Provide a detailed revenue projection that outlines the sources of revenue and the expected growth trajectory over the next few years. Clearly explain the factors driving revenue growth and the assumptions made.
- Expense Projections: Present a breakdown of projected expenses, including operating costs, marketing, research and development, and other key expenditure categories. Justify each expense based on the company’s growth strategy.
- Cash Flow Management: Illustrate how the startup plans to manage its cash flow to ensure financial stability and support ongoing operations. Highlight measures to address any potential cash flow challenges.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Include a sensitivity analysis that assesses how changes in key assumptions or market conditions might impact the financial projections. This analysis demonstrates the startup’s awareness of potential risks and uncertainties.
- Profitability and Growth Metrics: Highlight key profitability metrics, such as gross profit margins, net profit margins, and return on investment (ROI). Discuss the company’s strategies to improve profitability over time.
- Capital Needs and Funding Strategy: Clearly state the startup’s capital requirements to achieve the projected growth. Outline the funding strategy, including potential funding sources, such as angel investors, venture capital, or strategic partnerships.
- Contingency Plans: Address potential challenges or roadblocks that could impact the achievement of financial projections. Present contingency plans that show how the startup will adapt to changing market conditions or unforeseen events.
Step 6: Assess Market Analysis and Growth Potential
For startups, market analysis and growth potential play a pivotal role in the due diligence process. Investors want to understand the target market, the competitive landscape, and the startup’s unique value proposition. Demonstrating a clear understanding of the market and a compelling growth strategy can significantly influence investment decisions.
Here are the essential components to consider when assessing market analysis and growth potential during due diligence:
- Market Size and Opportunity: Provide an in-depth analysis of the target market’s size, trends, and growth prospects. Present data and research supporting the market’s potential and how the startup plans to capture a share of it.
- Competitive Analysis: Identify key competitors in the market and evaluate their strengths and weaknesses. Differentiate the startup’s offerings and value proposition from competitors to highlight its competitive advantage.
- Target Customer Profile: Define the ideal customer profile and demonstrate a deep understanding of their needs, pain points, and preferences. Explain how the startup’s products or services address these customer needs uniquely.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy: Present the startup’s marketing and sales strategy, including customer acquisition channels, pricing models, and sales projections. Discuss any successful marketing initiatives or partnerships that have already been established.
- Customer Retention and Satisfaction: Share metrics and strategies related to customer retention and satisfaction. Highlight customer feedback and testimonials to showcase the startup’s ability to build and maintain strong customer relationships.
- Industry Trends and Disruptions: Stay informed about industry trends and potential disruptions that could impact the startup’s growth. Address how the company plans to adapt and stay ahead in a rapidly evolving market.
Step 7: Evaluate Operational Efficiency and Scalability
Demonstrating a well-structured and scalable operational model can assure investors that the startup is poised for long-term success. Here are a few pointers for you to go through:
- Provide an overview of the startup’s core business processes and workflow, highlighting areas where the company has implemented streamlined and efficient procedures.
- Assess the technology infrastructure in place to support business operations, discussing the software, tools, and systems used to optimize productivity and enhance customer experience.
- Demonstrate effective resource allocation, including manpower, equipment, and capital investments, showing how resources align with growth objectives and strategic priorities.
- Evaluate the startup’s supply chain, including sourcing, production, and distribution processes, addressing any potential risks or dependencies on key suppliers.
- Showcase the startup’s commitment to quality control and assurance measures, discussing how the company maintains product or service excellence and manages customer feedback.
- Present a clear plan for scaling the business to meet increasing demand, addressing how the startup plans to expand production, personnel, and distribution capabilities as the company grows.
- Share key operational metrics and performance indicators, such as lead times, inventory turnover, and customer response times, using data to demonstrate operational effectiveness and improvements over time.
- Address potential operational risks and how the startup mitigates them, showing how the company maintains business continuity and manages unforeseen challenges.
Step 8: Review Customer and Supplier Relationships
These relationships are vital indicators of the company’s market positioning, revenue stability, and overall business health. A strong and loyal customer base, as well as reliable supplier partnerships, can significantly impact the startup’s growth potential and attractiveness to investors.
Key considerations include:
- Customer Base and Segmentation: Provide an overview of the startup’s customer base, including its size, demographics, and geographic distribution. Discuss any customer segmentation strategies employed to target specific market segments effectively.
- Customer Retention and Satisfaction: Share metrics related to customer retention rates and satisfaction levels. Present any customer feedback mechanisms and actions taken based on customer input.
- Customer Acquisition Strategy: Explain the startup’s customer acquisition strategy, including marketing channels and tactics used to attract new customers. Address how the company plans to expand its customer base over time.
- Key Customer Relationships: Highlight any significant or long-standing customer relationships contributing significantly to the startup’s revenue. Address how the company maintains and nurtures these relationships.
- Supplier Partnerships: Evaluate the startup’s relationships with suppliers, especially those providing critical inputs or resources for the business. Discuss the terms and conditions of supplier agreements and any measures in place to manage supplier risks.
- Supply Chain Stability: Assess the stability of the startup’s supply chain and its ability to meet demand fluctuations. Address any contingency plans to address potential supply chain disruptions.
- Payment Terms and Receivables: Review the startup’s payment terms with customers and the status of outstanding receivables. Discuss measures taken to manage cash flow and mitigate payment delays.
- Supplier Diversity and Alternatives: Evaluate the startup’s supplier diversity and the availability of alternative suppliers. Address any potential dependencies on a single supplier and plan to diversify the supplier base.
Step 9: Investment Terms and Exit Strategy
In the final stage of due diligence for startups, investors focus on evaluating the investment terms. Providing transparency can favor investment terms.
Investment Terms and Conditions:
Share the terms and conditions of the proposed investment, including any preferred stock rights, liquidation preferences, and anti-dilution provisions. Discuss how the investment aligns with the startup’s overall capital structure.
Exit Strategy:
Address the startup’s exit strategy and how the investor can expect to realize returns on their investment. Discuss potential exit options, such as acquisition, IPO, or buyback.
Don’t Worry if You Don’t Tick All Those Boxes
Angel investors understand that startups are at different stages of development. Some may be well-established, while others are still working on their proof-of-concept. The eight topic areas mentioned earlier are general guidelines for what your prospective angel investor may explore during due diligence. Rest assured, your investor won’t reject you just because you haven’t filed a patent for your IP.
However, they will be concerned if they discover that your company lacks the legal right to market or sell the IP. Focus on presenting your startup’s strengths and potential, and investors will evaluate your unique situation with that in mind.
To Sum It Up
Remember the importance of under-promising and over-delivering. Conservative projections that later reveal the potential for even higher returns will excite investors. On the other hand, making ambitious claims that don’t hold up during due diligence may dampen their enthusiasm.
Promptly responding to investor inquiries is crucial. Even a simple acknowledgment with an estimated time of when you’ll provide the requested information demonstrates your commitment to the process and fosters confidence in your professionalism.
